How Masca Uses Ceramic for Verifiable Credential Storage
Masca is a MetaMask Snap that provides a straightforward way for users to manage their identity, data and attestations.

Masca is an open-source, decentralized identity wallet that lets you manage your off-chain identifiers and attestations. It is a MetaMask Snap plugin for MetaMask that extends its base functionalities for decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and verifiable credentials (VCs)—turning MetaMask into an identity hub.
Masca is developed by Blockchain Lab:UM, an R&D laboratory specializing in blockchain technology, decentralized identity, and decentralized artificial intelligence.
Ceramic, as one of the supported storage solutions in Masca, plays a crucial role in enabling users to store their data, have it available on different devices, and will serve as a foundation for data interoperability with other projects in the future.
Decentralized Identity and Data Management With Masca
As decentralized applications (dApps) and other decentralized solutions become more complex and personalized for users, there is a growing need to manage user identity and associated data. Given that the amount of data is expected to grow exponentially, off-chain solutions are essential to handle this vast amount in a scalable, efficient, and inexpensive way.
For quite some time, MetaMask has been working on a feature called MetaMask Snaps—a system that enables extended functionalities of the base MetaMask with Snaps. Snaps are JavaScript programs, each running in its own isolated execution environment inside MetaMask, and can run arbitrary logic, thus significantly extending the functionality of MetaMask.
How Does Masca Work?
Masca is a MetaMask Snap that provides a straightforward way for users to manage their identity, data and attestations. At the same time, Masca also offers dApp developers a simple-to-use interface to integrate decentralized identity functionalities into their applications. There are (almost) endless attestation types, but some examples are conference attendance, government, KYC, education, and various gaming credentials.
The decentralized identity space is still in a somewhat early stage, various solutions and protocols are being developed and tested. Masca offers flexibility with multiple integrations for developers to choose what suits their use cases and needs. Masca supports multiple DID methods (did:pkh, did:ethr, did:key, did:jwk, did:polygonid, etc.) and cryptographically-signed data formats (JWT, JSON-LD, EIP712). Some of the integrated projects include Ceramic Network, Polygon ID, and EBSI.
Masca uses Veramo Client for DID management, as well as for the creation, presentation, and validation of Verifiable Credentials. In alignment with Masca’s mission, the snap also offers flexibility around data storage, allowing users to toggle between the local MetaMask Snap state (which exists fully off-chain and exclusively in the user’s browser), as well as storage on the Ceramic Network.
Masca was successfully rolled out during the Open Beta release of MetaMask Snaps in September 2023. For more information, you can visit this link and the Snaps directory.
What issues did Masca face before using Ceramic?
In the beginning, users could only store their data locally, which meant directly in their MetaMask wallet in the encrypted storage. But that presents a problem when switching to different devices (using the same seed phrase), because the data is unavailable and not synchronized. It also was not possible if users want to share their data in a structured and composable way, which is why Masca chose to build on and integrate Ceramic.
“Ceramic Network is a data ledger that builds on IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) and creates an abstraction layer that makes it much more suitable for endless use cases, one of them being data vaults for identity data.”- Masca team
Why Masca Chose Ceramic
Ceramic offers a scalable network for data, builds on top of the same primitives as Masca (DIDs), and provides developer-friendly tools for development. Structuring the otherwise unstructured data into data streams, controlled by user accounts, creates a powerful solution for managing identity data.
Ceramic also has a broad ecosystem of projects working on diverse challenges and problems. By being part of this ecosystem, the Masca team says it aims to connect with other projects in the identity space and work together to tackle those challenges, such as conforming to the same data models and making data truly composable across different applications. Building more rich and complex decentralized identities can also help solve the challenges with reputation and Sybil attacks in the future.
How Masca Uses Ceramic
Masca is now live on Ceramic Mainnet! Ceramic is currently used in the Masca ecosystem for two primary purposes:
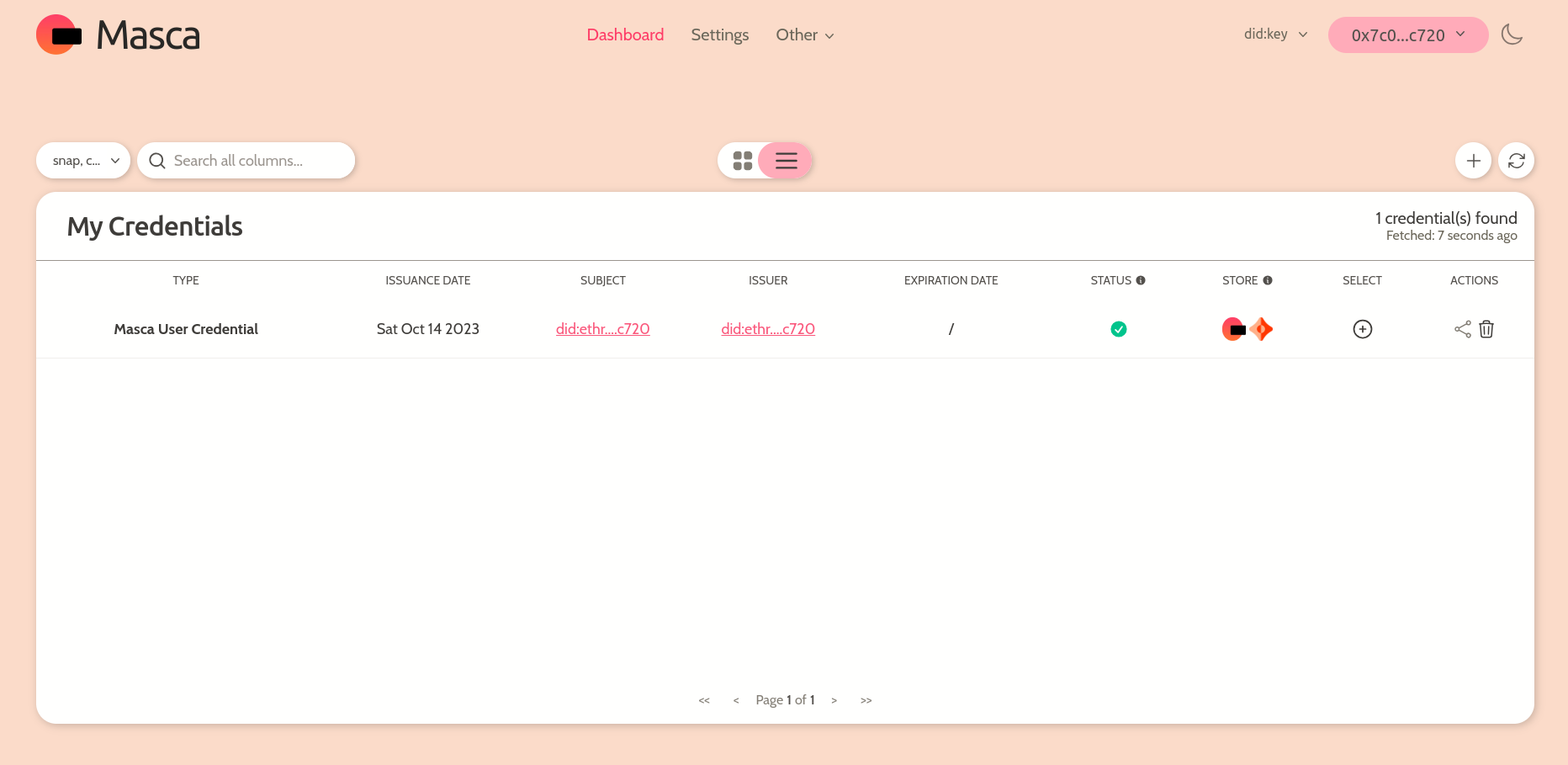
- Verifiable Credential Storage: Since VCs are off-chain attestations, users must store them somewhere. Ceramic offers a scalable way to store attestations.
- Schemas: Each VC has a strictly defined structure and data model, which are defined with schemas. Using schemas, VCs of the same type are consistent across different applications.
Users can freely migrate their credentials between Snap-encrypted storage and Ceramic Network as they wish. Selection of storage most often depends on the type of attestations and level of security/privacy needed.
Masca has several exciting features in the pipeline, such as:
- Enabling users to store encrypted data
- Supporting selective disclosure for VCs
- Adding support for ComposeDB on Ceramic
The Masca team is excited to work with other projects in the Ceramic ecosystem and help contribute to the world's composable data stack.
Create Your Credential
Visit Masca to create your decentralized identity and first off-chain verifiable credential. You can store the credential on Ceramic and make it available to share across dApps that integrate Masca (such as ReputeX) or those that use Ceramic. If you’re a dev interested in integrating Masca into your application, check out the documentation page.
Decentralized identity is becoming a core element of the decentralized web, addressing the challenge of verifying data in the ever-increasing volume of content generated. Masca's upcoming migration to ComposeDB will further improve data management and interoperability.

